What Causes Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation refers to the natural coloration of the skin, which is determined by the presence of melanin, a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes. While skin pigmentation is primarily determined by genetics, various internal and external factors can influence its development and distribution. Understanding the basics of skin pigmentation and its significance in overall skin health is essential for recognizing the factors that contribute to pigmentation irregularities and addressing them effectively.
Understanding the Basics
Melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, is produced by melanocytes located in the basal layer of the epidermis. There are two main types of melanin: eumelanin, which imparts brown or black color to the skin, and pheomelanin, which produces red or yellow tones. The production and distribution of melanin are regulated by various factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, and exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Skin pigmentation plays a crucial role in protecting the skin from UV damage, regulating body temperature, and providing a defense against environmental insults.
Importance of Skin Pigmentation
Maintaining healthy skin pigmentation is essential for both aesthetic and functional reasons. Properly pigmented skin not only contributes to a person's physical appearance but also serves as a protective barrier against harmful UV radiation and environmental pollutants. Pigmentation irregularities, such as hyperpigmentation (excessive darkening of the skin) or hypopigmentation (loss of skin color), can have significant psychological and social implications, affecting an individual's self-esteem and quality of life. Understanding the factors that influence skin pigmentation is crucial for addressing pigmentation concerns effectively and promoting overall skin health and well-being.
Factors Contributing to Skin Pigmentation
Genetic Factors:
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in determining an individual's skin color and susceptibility to pigmentation disorders. Variations in genes responsible for melanin production, such as MC1R and TYR, can influence the amount and type of melanin produced by melanocytes. Certain ethnicities are more prone to specific pigmentation traits, with individuals of African, Asian, and Hispanic descent often exhibiting darker skin tones due to increased melanin production.
Sun Exposure:
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is one of the most significant external factors influencing skin pigmentation. UV radiation stimulates melanocytes to produce melanin as a protective response to shield the skin from UV damage. Prolonged or excessive sun exposure can lead to increased melanin production, resulting in tanning or hyperpigmentation. Additionally, repeated sun exposure without adequate protection can contribute to premature aging, sunspots, and other pigmentation irregularities.
Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause, can impact skin pigmentation. Pregnancy-related hormonal changes can trigger a condition known as melasma or chloasma, characterized by the development of dark patches on the face. Hormonal contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy may also influence melanin production, leading to changes in skin pigmentation.
Age:
Aging is associated with changes in skin pigmentation due to a combination of intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Intrinsic aging leads to a gradual decline in melanocyte function and melanin production, resulting in the loss of skin color and the development of age-related hypopigmentation. Extrinsic aging, caused by factors such as sun exposure and environmental pollutants, can exacerbate pigmentation irregularities, contributing to the formation of age spots, freckles, and uneven skin tone.
Inflammatory Conditions:
Inflammatory skin conditions, such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis, can disrupt normal melanin production and distribution, leading to pigmentation changes. Inflammatory mediators released during the inflammatory process can stimulate melanocytes, resulting in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) characterized by dark patches or spots on the skin. Chronic inflammation can also contribute to long-term pigmentation irregularities and skin damage if left untreated.
Overall, a combination of genetic, environmental, hormonal, and age-related factors influences skin pigmentation. Understanding these factors is essential for effectively managing pigmentation concerns and maintaining healthy, radiant skin. By adopting sun protection measures, managing hormonal imbalances, and addressing inflammatory skin conditions, individuals can minimize the risk of pigmentation irregularities and promote skin health and vitality.
Role of Melanin in Skin Pigmentation
Melanin, produced by melanocytes, determines skin, hair, and eye color, varying among ethnicities. Understanding melanin's role is vital for addressing pigmentation disorders. Melanocytes, in the epidermis's basal layer, synthesize melanin from tyrosine via enzymatic processes involving tyrosinase, TRP-1, and TRP-2, forming melanosomes transferred to keratinocytes. Eumelanin yields brown/black pigments predominant in darker skin, while pheomelanin produces red/yellow hues in lighter skin. Melanocytes respond to stimuli like UV radiation, regulating melanin production through intricate signaling pathways. Dysfunctions can cause pigmentation disorders. Recognizing melanin's significance aids in effectively managing such conditions.
Environmental Influences on Skin Pigmentation
UV Radiation:
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is one of the primary environmental factors influencing skin pigmentation. UV radiation stimulates melanocytes to produce melanin as a protective response to shield the skin from UV damage. Prolonged or excessive sun exposure can lead to increased melanin production, resulting in tanning or hyperpigmentation. Additionally, chronic sun exposure can contribute to the formation of sunspots, freckles, and other pigmentation irregularities.
Pollution:
Environmental pollutants, such as particulate matter, heavy metals, and chemicals found in air pollution, can also impact skin pigmentation. Pollution exposure can trigger oxidative stress and inflammation in the skin, leading to the activation of melanocytes and alterations in melanin production. Long-term exposure to pollutants may exacerbate existing pigmentation disorders and contribute to the development of hyperpigmentation or uneven skin tone.
Chemical Exposure:
Chemical exposure from skincare products, cosmetics, and household cleaners can influence skin pigmentation. Certain chemicals, such as hydroquinone, retinoids, and alpha hydroxy acids, are known to affect melanin synthesis and distribution in the skin. Prolonged use or misuse of these products may lead to pigmentation irregularities, including hyperpigmentation, skin sensitivity, and irritation. It's essential to choose skincare products carefully and avoid overexposure to potentially harmful chemicals to maintain healthy skin pigmentation.
Medical Conditions Associated with Skin Pigmentation:
Hyperpigmentation:
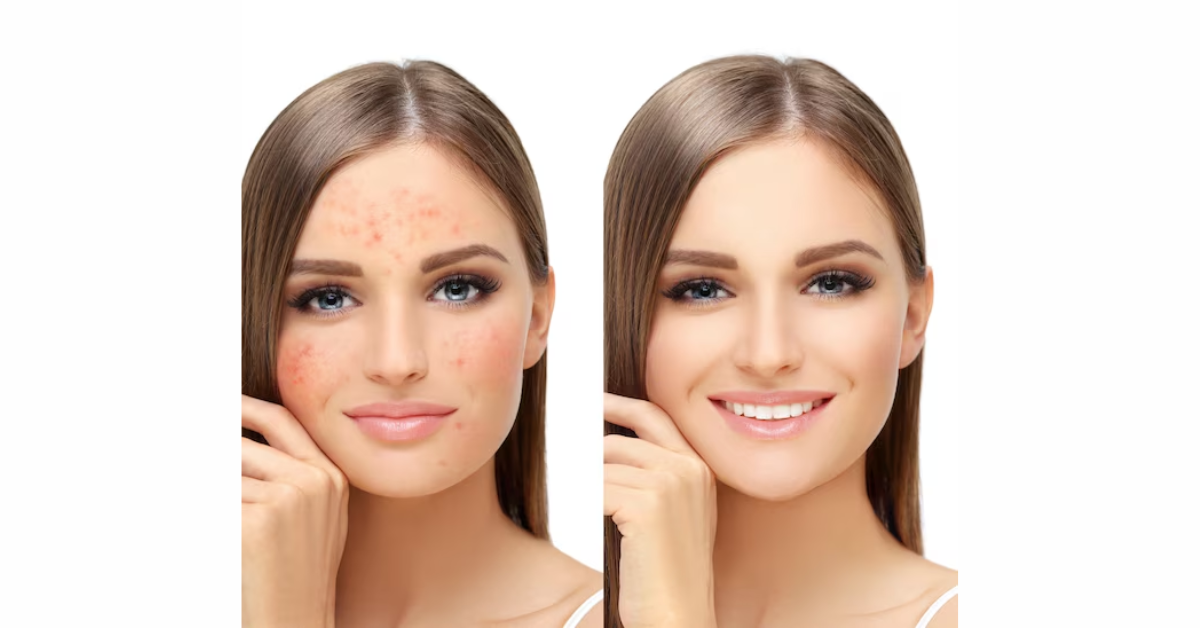
Hyperpigmentation refers to the darkening of the skin caused by the overproduction of melanin. Common types of hyperpigmentation include sunspots, melasma, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). Hyperpigmentation can result from various factors, including sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, and certain medical conditions or medications. Treatment options for hyperpigmentation may include topical creams, chemical peels, laser therapy, or other light-based treatments.
Hypopigmentation:
Hypopigmentation is characterized by the loss of skin color due to a reduction in melanin production or distribution. Conditions such as vitiligo, albinism, and certain autoimmune disorders can cause hypopigmentation. Vitiligo, in particular, is a chronic skin condition characterized by the development of white patches on the skin due to the destruction of melanocytes. Treatment for hypopigmentation may include topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, or surgical procedures to restore pigment to affected areas.
Melasma:
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by the development of brown or gray patches on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. Hormonal changes, sun exposure, and genetic predisposition are believed to contribute to the development of melasma. Treatment options for melasma may include topical bleaching agents, chemical peels, or laser therapy to reduce pigmentation and even out skin tone.
Vitiligo:
Vitiligo is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by the loss of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) in certain areas of the skin, resulting in white patches or depigmentation. The exact cause of vitiligo is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, autoimmune, and environmental factors. Treatment for vitiligo may include topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, depigmentation therapy, or surgical interventions such as skin grafting.
Prevention and Management Strategies
To prevent pigmentation issues, prioritize sun protection by applying broad-spectrum SPF 30 sunscreen daily, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding tanning beds. A consistent skincare routine tailored to your skin type is crucial, involving twice-daily cleansing and exfoliation to promote cell turnover. Incorporate products with vitamin C, niacinamide, retinoids, and AHAs to even out skin tone. Treatment options include topical treatments like hydroquinone and professional treatments such as chemical peels and laser therapy. Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice. Consistency and patience are key to achieving lasting results and maintaining skin health and radiance.
Pigmentation Treatment at Malka Med Spa
At Malka Med Spa, we offer effective pigmentation treatment starting with a thorough consultation where our expert team assesses your skin type, concerns, and desired outcomes to create a personalized treatment plan. Utilizing cutting-edge skincare technology including laser therapies and chemical peels, we target pigmentation irregularities directly. Each treatment plan is customized to address individual needs, whether it's sun spots, melasma, or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. With our professional expertise in dermatology and skincare, we prioritize safety and efficacy, ensuring the highest quality care throughout your journey. Our results-oriented approach focuses on achieving clear, radiant skin, monitoring progress closely and adjusting treatments as needed. Experience the difference at Malka Med Spa and say goodbye to pigmentation concerns.
Conclusion
Understanding the factors influencing skin pigmentation and adopting appropriate prevention and management strategies are essential for maintaining healthy, radiant skin. Throughout this discussion, we've highlighted the importance of sun protection, a consistent skincare routine, and various treatment options for managing pigmentation irregularities. By recapping the key points discussed and emphasizing the significance of skin pigmentation awareness, we empower individuals to take proactive steps in caring for their skin and achieving a balanced, luminous complexion. With knowledge, diligence, and a commitment to skin health, we can embrace our unique pigmentation and confidently navigate our skincare journey for long-term beauty and well-being.