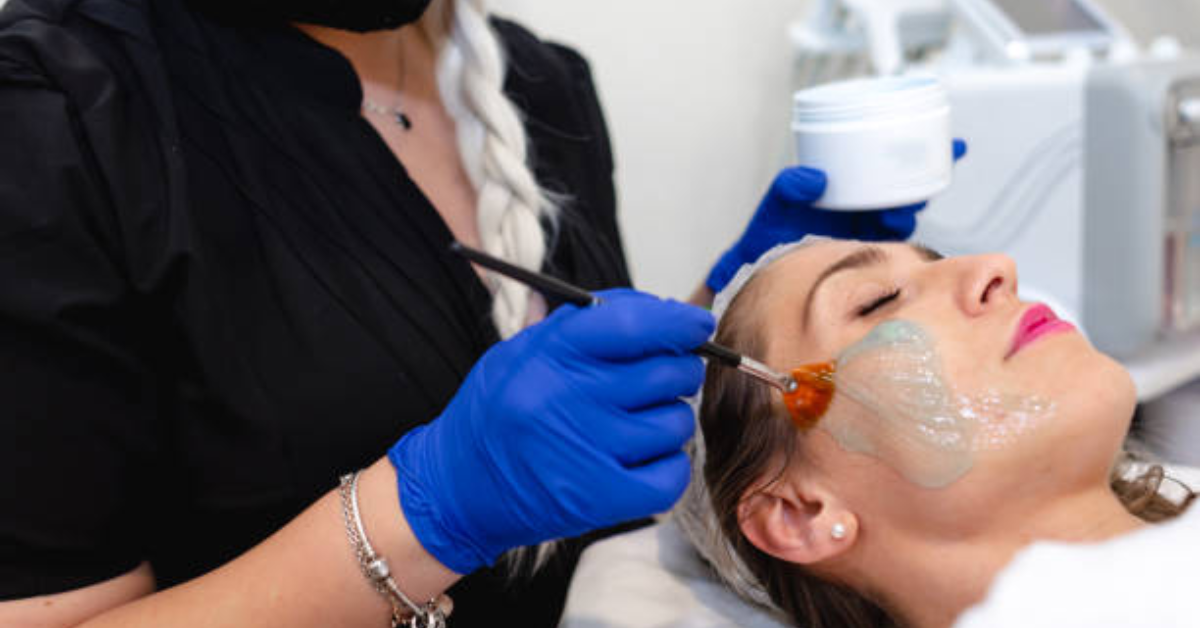
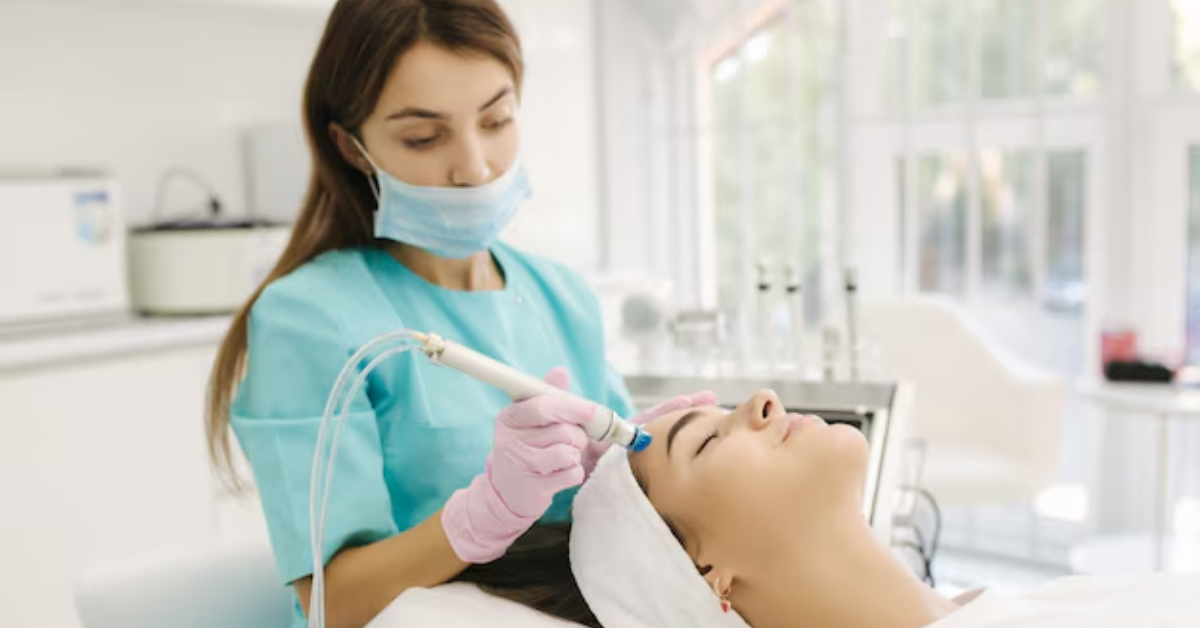
How To Get Rid of Pigmentation?
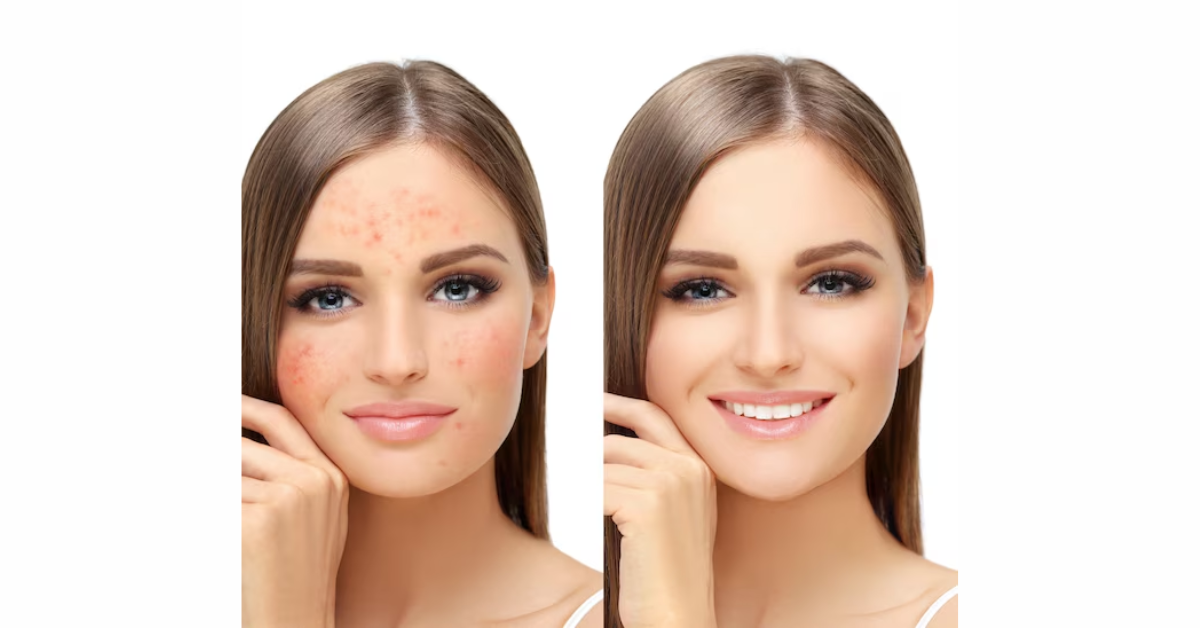
Dealing with pigmentation can be a frustrating and challenging aspect of skincare for many individuals. Understanding pigmentation, its causes, and effective methods for its removal or reduction is crucial for achieving clearer, more even-toned skin. Pigmentation refers to the discoloration of the skin caused by the overproduction or uneven distribution of melanin, the pigment responsible for giving skin its color. While melanin is essential for protecting the skin from harmful UV radiation, its irregular accumulation can lead to various forms of pigmentation issues, including dark spots, freckles, melasma, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
What is Pigmentation?
Pigmentation manifests in various forms and severities, from minor blemishes to pronounced patches of discoloration, necessitating a thorough understanding for appropriate treatment. Common types include dark spots, also known as age or sunspots, resulting from prolonged sun exposure, characterized by small, flat patches of darker skin; freckles, genetic in nature, appearing as small areas of increased melanin production that intensify with sun exposure; melasma, marked by larger, irregular patches of brown or grayish pigmentation on the face, often exacerbated by hormonal changes like pregnancy or contraceptive use; and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), emerging after skin inflammation or injury such as acne or burns, presenting as dark spots or patches post-healing.
Types of Pigmentation
Pigmentation issues manifest in various forms, each with its own characteristics and
underlying causes. Understanding these types of pigmentation is crucial for implementing targeted treatment strategies. Here are some common types:
Hyperpigmentation: This refers to the darkening of the skin due to an overproduction of melanin. Hyperpigmentation can occur in small patches, such as freckles or age spots, or larger areas, such as melasma. Common causes include sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, and genetics.
Hypopigmentation:
In contrast to hyperpigmentation, hypopigmentation involves the loss or reduction of skin color. This can result in lighter patches of skin compared to the surrounding areas. Causes of hypopigmentation may include damage to melanocytes (cells responsible for producing melanin), autoimmune conditions, skin injuries, or certain medical treatments like laser therapy.
Melasma: Melasma presents as brown or grayish patches, usually on the face, and is commonly associated with hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or the use of oral contraceptives. Sun exposure often exacerbates melasma. It is characterized by symmetrical pigmentation on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip.
Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH):
PIH occurs as a result of skin trauma or inflammation, such as acne, cuts, burns, or other injuries. It is characterized by dark spots or patches that develop after the initial injury has healed. PIH can affect individuals of all skin types but is more common in darker skin tones.
Freckles: Freckles are small, concentrated areas of increased melanin production and are typically genetic in nature. They often appear on areas of the skin that are regularly exposed to the sun, such as the face, shoulders, and arms.
Prevention of Pigmentation
Preventing pigmentation issues involves adopting proactive skincare practices and lifestyle habits to minimize the risk of melanin overproduction or uneven distribution. UV radiation from the sun is a major contributor to pigmentation problems. To protect your skin, apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days. Wear protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeved shirts, and seek shade during peak sun hours.
Establishing a comprehensive skincare routine can help maintain skin health and minimize the risk of pigmentation issues. This includes cleansing the skin daily to remove dirt, oil, and impurities, followed by the application of antioxidant-rich serums or creams to neutralize free radicals and prevent oxidative damage. Incorporate products containing ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, and alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) to promote skin cell turnover and reduce the appearance of pigmentation.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can help safeguard your skin against the development of pigmentation problems and maintain a clearer, more radiant complexion.
Home Remedies for Pigmentation
Many individuals prefer natural remedies for pigmentation as they are often gentle on the skin and can be easily incorporated into skincare routines. Here are some home remedies using natural ingredients and DIY treatments:
Lemon Juice: Lemon juice contains citric acid, which has natural bleaching properties that can help lighten dark spots and hyperpigmentation. Apply freshly squeezed lemon juice to the affected areas using a cotton ball and leave it on for about 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with lukewarm water. However, lemon juice can be irritating to sensitive skin, so it's essential to dilute it with water or honey before application.
Aloe Vera: Aloe vera gel is known for its soothing and healing properties, making it an excellent remedy for various skin concerns, including pigmentation. Apply fresh aloe vera gel directly to the affected areas and leave it on overnight. Regular use can help reduce inflammation and lighten dark spots over time.
Turmeric:
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Create a paste by mixing turmeric powder with water or yogurt and apply it to pigmented areas. Leave it on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing off with water. Be cautious as turmeric can temporarily stain the skin yellow.
Apple Cider Vinegar:
Apple cider vinegar contains acetic acid, which may help lighten dark spots and improve overall skin tone. Dilute apple cider vinegar with water in a 1:1 ratio and apply it to pigmented areas using a cotton ball. Leave it on for a few minutes before rinsing off. Start with a patch test to ensure your skin tolerates it well.
Professional Treatments for Pigmentation:
While home remedies can be effective for mild pigmentation issues, professional treatments administered by dermatologists or skincare professionals offer more targeted and potent solutions. Here are some common professional treatments for pigmentation:
Chemical Peels:
Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin, which exfoliates the outer layer and promotes cell turnover. This helps reduce the appearance of pigmentation, including dark spots and uneven skin tone. Different types of peels are available, ranging from superficial to deep, depending on the severity of the pigmentation and desired results.
Laser Therapy:
Laser treatments target pigmented areas with high-energy light beams, breaking down excess melanin and stimulating collagen production. This can help lighten dark spots, melasma, and other forms of pigmentation. Various types of lasers are used, including fractional lasers, Q-switched lasers, and intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy, each with specific benefits and considerations.
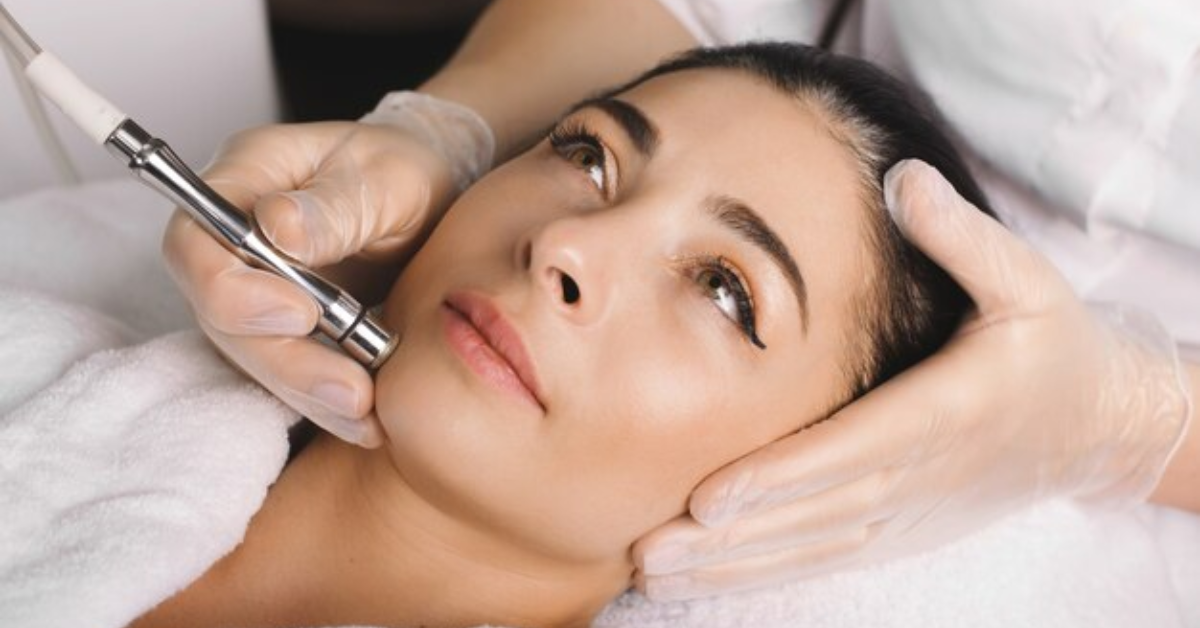
Microdermabrasion:
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive exfoliation technique that uses a device to gently remove the outer layer of dead skin cells, revealing smoother, more even-toned skin underneath. While it may not be as effective for deep pigmentation, it can help improve the appearance of mild to moderate pigmentation issues and enhance the penetration of skincare products applied afterward.
Before undergoing any professional treatment for pigmentation, it's essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the most suitable option based on your skin type, concerns, and treatment goals. Additionally, proper skincare maintenance and sun protection are crucial for optimizing and prolonging the results of professional treatments.
Skincare Tips for Pigmentation
Managing pigmentation requires a consistent skincare routine and mindful lifestyle choices. When selecting skincare products for pigmentation, look for ingredients that target melanin production and promote skin brightening. Key ingredients to consider include:
Vitamin C: Known for its antioxidant properties, vitamin C helps inhibit melanin production and fade dark spots.
Niacinamide (Vitamin B3): Niacinamide can help regulate melanin production and improve overall skin tone.
Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs): These exfoliating acids help remove dead skin cells, promote cell turnover, and fade pigmentation.
Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent that can effectively reduce the appearance of dark spots, but it should be used with caution and under the guidance of a dermatologist.
Retinoids: Retinoids, such as retinol or prescription-strength tretinoin, help stimulate collagen production, promote cell turnover, and fade pigmentation over time.
Daily Skincare Routine: Establishing a daily skincare routine is essential for managing pigmentation and maintaining overall skin health. A basic skincare routine for pigmentation may include:
- Use a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and impurities from the skin without stripping away its natural oils.
- Apply a targeted treatment containing ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, or hydroquinone to pigmented areas.
- Hydrate the skin with a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep it soft and supple.
- Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every morning, even on cloudy days, to protect the skin from UV radiation, which can exacerbate pigmentation.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Pigmentation:
In addition to a consistent skincare routine, certain lifestyle changes can help manage pigmentation and promote overall skin health. Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to provide essential nutrients that support skin health. Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts, can help protect the skin from oxidative damage and promote healing. Consider incorporating foods rich in vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene into your diet to support skin regeneration and repair.
Chronic stress can trigger hormonal imbalances and inflammation, which may exacerbate pigmentation issues. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies and activities you enjoy. Prioritize self-care and make time for relaxation to help maintain a healthy balance in your life.
Consultation with a Dermatologist
Seeking professional advice from a dermatologist is crucial for effectively managing pigmentation issues. Dermatologists are medical experts specializing in skin health and conditions. They have the knowledge and experience to accurately diagnose pigmentation problems, identify underlying causes, and recommend appropriate treatment options. Consulting a dermatologist ensures that you receive accurate information and personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs and concerns.
One of the significant advantages of consulting a dermatologist is the ability to receive a customized treatment plan designed to address your unique pigmentation issues. Dermatologists can recommend a comprehensive approach that may include professional treatments, prescription medications, and personalized skincare routines based on your skin type, severity of pigmentation, and treatment goals.
For comprehensive pigmentation treatments and expert guidance, consider consulting Malka Med Spa. With their extensive range of advanced skincare services and experienced professionals, Malka Med Spa offers tailored solutions to address various pigmentation concerns effectively. From chemical peels and laser therapy to microdermabrasion and personalized skincare regimens, their team can create a customized treatment plan to help you achieve clearer, more radiant skin.
Conclusion
Managing pigmentation requires a multifaceted approach that combines effective skincare practices, lifestyle adjustments, and, when necessary, professional intervention. By understanding the causes of pigmentation and implementing preventive measures, such as sun protection and proper skincare, you can minimize the risk of pigmentation issues. However, for those already experiencing pigmentation concerns, seeking guidance from a dermatologist, such as those at Malka Med Spa, is essential for receiving personalized treatment plans and achieving optimal results.