Is Laser Treatment Safe For Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation is a common concern that affects individuals of all ages and ethnicities. It refers to the discoloration or unevenness of the skin tone, which can be caused by various factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, genetics, and skin conditions like melasma or hyperpigmentation. These pigmentation issues not only affect the appearance but also can impact one's self-confidence and quality of life.
In the quest for clearer and more even-toned skin, many individuals turn to different treatment options, one of which is laser therapy. Laser treatment has gained popularity as an effective method for addressing skin pigmentation concerns. By utilizing advanced laser technology, dermatologists and skincare professionals can target specific areas of pigmentation with precision, promoting a more uniform complexion.
It is crucial for individuals considering laser treatment for their pigmentation concerns to understand its safety and efficacy. By providing a comprehensive overview of laser therapy, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about their skincare journey. Whether you're dealing with age spots, sun damage, or other pigmentation issues, this article will serve as a valuable resource to help you navigate the world of laser treatment for skin pigmentation.
What is Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation refers to the natural color of the skin, which is determined by the amount of melanin produced by specialized cells called melanocytes. Melanin is a pigment responsible for giving skin its color and protecting it from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Skin pigmentation can vary widely among individuals and is influenced by genetics, ethnic background, and environmental factors.
Causes of skin pigmentation
Skin pigmentation disorders can arise due to various factors, including:
Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can stimulate melanin production, leading to tanning or hyperpigmentation. Conversely, inadequate protection from UV rays can result in sunburn and uneven pigmentation.
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as during pregnancy or menopause, can trigger changes in melanin production, causing conditions like melasma or chloasma (also known as pregnancy mask).
Genetics: Genetic factors play a significant role in determining an individual's skin color and susceptibility to certain pigmentation disorders.
Inflammation and Injury: Skin trauma, inflammation, or injury can sometimes result in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, where dark spots or patches develop at the site of the injury.
Ageing: As we age, the skin's ability to produce melanin may decrease, leading to the formation of age spots or uneven pigmentation.
Types of skin pigmentation disorders
There are several types of skin pigmentation disorders, including:
Hyperpigmentation:
Characterized by the darkening of patches of skin due to excess melanin production. Common forms of hyperpigmentation include sunspots, melasma, and freckles.
Hypopigmentation: In contrast to hyperpigmentation, hypopigmentation refers to areas of skin that are lighter or depigmented due to a lack of melanin production. Conditions such as vitiligo and albinism are examples of hypopigmentation disorders.
Uneven Pigmentation: This includes conditions where the skin exhibits irregular distribution of melanin, resulting in patches of varying colors or tones.
Understanding these factors is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach for managing skin pigmentation disorders.
Laser Treatment: How Does It Work?
Laser treatment for skin pigmentation involves the use of focused laser beams to target and selectively destroy melanin-containing cells or break down pigment particles within the skin. This process helps to reduce the appearance of dark spots, freckles, and other pigmentation issues, while promoting a more even skin tone.
The mechanism of action of laser treatment for skin pigmentation varies depending on the specific type of laser used. Generally, lasers emit high-energy light pulses that are absorbed by melanin in the skin. This leads to localized heating and destruction of melanin-containing cells, which are then naturally eliminated by the body's immune system. In some cases, lasers may also stimulate collagen production and skin rejuvenation, further improving skin texture and tone.
Types of lasers used
There are several types of lasers used in the treatment of skin pigmentation disorders, including:
Q-switched lasers: These lasers deliver short pulses of high-energy light that target specific pigments in the skin, such as melanin. Q-switched lasers are commonly used to treat conditions like melasma, sunspots, and tattoo removal.
Fractional lasers: Fractional laser technology delivers laser energy in a fractionated pattern, creating microthermal zones within the skin. This stimulates collagen production and promotes skin renewal, making it effective for treating both pigmentation issues and overall skin rejuvenation.
Alexandrite lasers:
Alexandrite lasers emit a specific wavelength of light that is highly absorbed by melanin, making them suitable for targeting pigmented lesions and hair removal.
Nd:YAG lasers:
Nd:YAG lasers are versatile devices that can penetrate deeper layers of the skin, making them effective for treating pigmentation disorders as well as vascular lesions and hair removal.
People with pigmentation concerns can make informed decisions about the best approach to addressing their pigmentation concerns by understanding how laser treatment works and the different types of lasers available. It's essential to consult with a qualified dermatologist or skincare professional to determine the best treatment plan based on your specific skin type, condition, and treatment goals.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Laser treatment for skin pigmentation may entail certain risks and side effects, including temporary discomfort, redness, swelling, and in rare cases, blistering or changes in skin texture. It's important for individuals considering laser treatment for skin pigmentation to discuss these potential risks and side effects with a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing the procedure. During the consultation process, the practitioner will assess the individual's skin type, medical history, and specific concerns to determine if laser treatment is the most suitable option.
Various factors can influence the safety of laser treatment for skin pigmentation, such as the type of laser used, the skill and experience of the practitioner, the individual's skin type and sensitivity, and adherence to pre- and post-treatment care instructions. Before undergoing laser treatment, individuals should take certain precautions, such as avoiding sun exposure and tanning beds, discontinuing the use of certain skincare products, disclosing any medical conditions or medications to the treating physician, and following any pre-treatment guidelines provided by the healthcare provider.
Efficacy of Laser Treatment
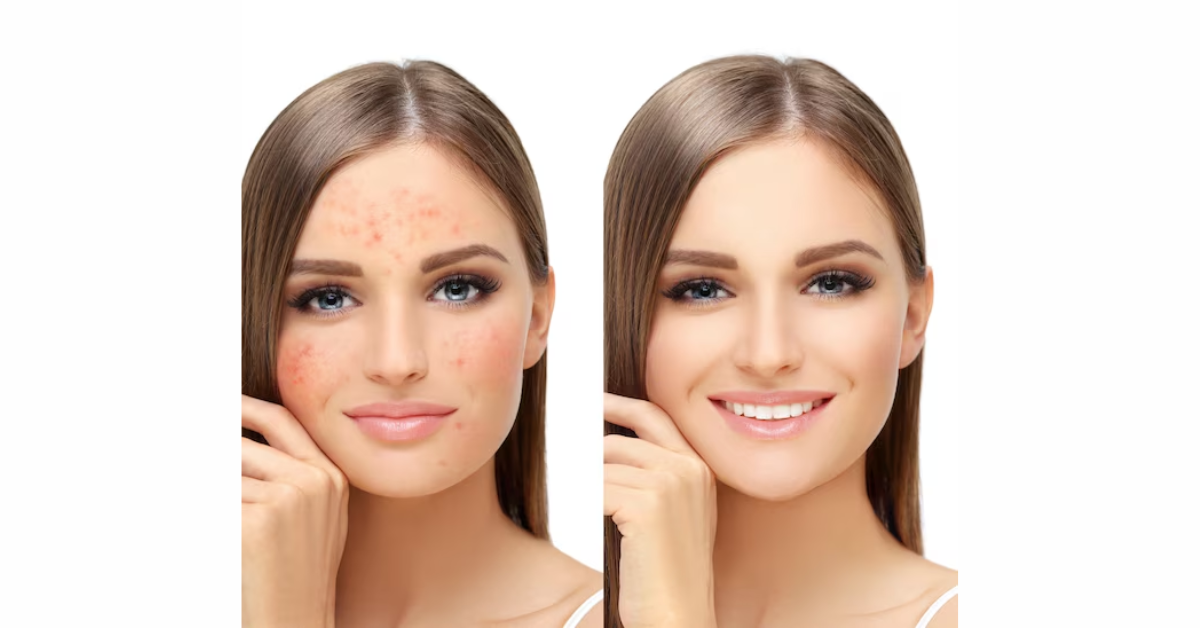
Laser treatment has been shown to be effective in addressing various types of skin pigmentation disorders, including hyperpigmentation, sunspots, melasma, and freckles. However, the efficacy of treatment may vary depending on factors such as the severity of the pigmentation, the type of laser used, and the individual's skin type and response to treatment.
While laser treatment can produce significant improvements in skin pigmentation, it's important to understand that results may vary from person to person. Success rates depend on factors such as the specific condition being treated, the number of treatment sessions, and individual factors such as skin type and lifestyle habits. Additionally, laser treatment may not completely eliminate pigmentation issues, and maintenance treatments may be necessary to maintain results over time.
Ideal Candidates For Laser Treatment
Ideal candidates for laser treatment for skin pigmentation are typically individuals who are in good overall health and have realistic expectations about the outcomes of the procedure. They may have concerns such as hyperpigmentation, sunspots, or uneven skin tone that they wish to address. Also, suitable candidates should have skin types that respond well to laser treatment and have not experienced adverse reactions to previous laser procedures.
Several factors may influence whether an individual is a suitable candidate for laser treatment, including skin type, skin sensitivity, medical history, medications being taken, and the severity of the pigmentation concern. Certain medical conditions or medications may increase the risk of complications or interfere with the effectiveness of the treatment. Additionally, individuals with darker skin tones may be at a higher risk of experiencing pigmentation changes or other adverse effects from laser treatment.
Consultation and Preparation
Consultation with a qualified dermatologist or skincare professional is crucial before undergoing laser treatment for skin pigmentation. During the consultation, the healthcare provider will assess the individual's skin type, medical history, and specific concerns to determine the most suitable treatment approach. They will also discuss the potential risks, benefits, and expected outcomes of the procedure, as well as address any questions or concerns the individual may have.
Before undergoing laser treatment, individuals may be advised to take certain preparatory steps to optimize the safety and effectiveness of the procedure. This may include avoiding sun exposure, discontinuing the use of certain skincare products or medications, and following any pre-treatment guidelines provided by the healthcare provider. Additionally, individuals should have realistic expectations about the outcomes of the treatment, understanding that multiple sessions may be required to achieve desired results and that maintenance treatments may be necessary to sustain improvements over time.
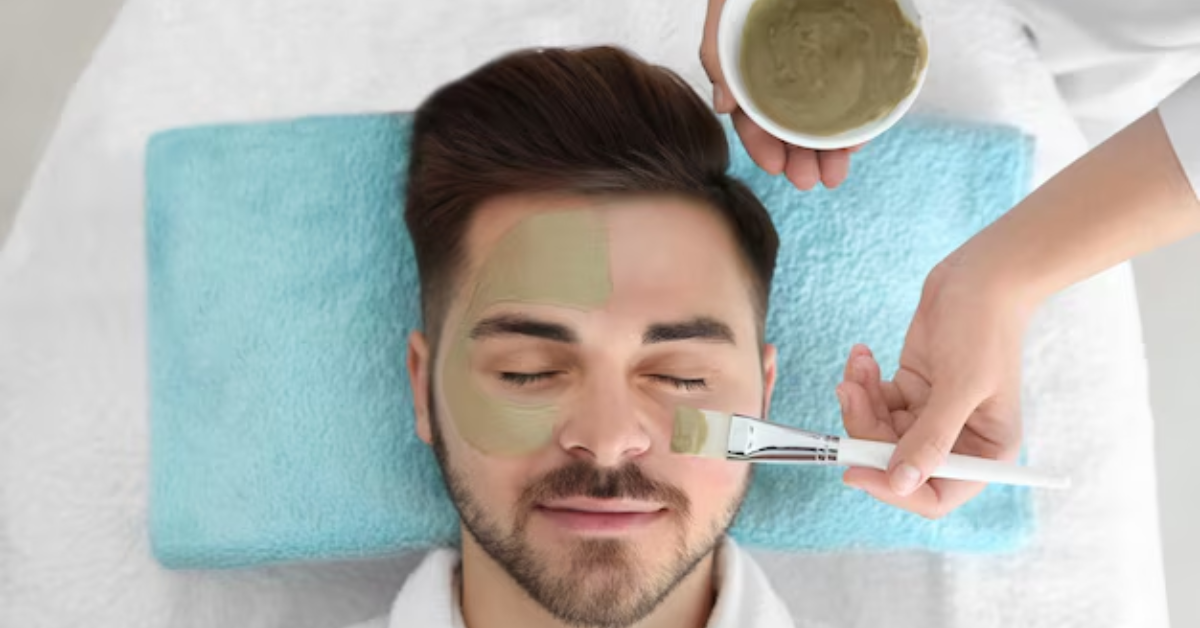
What To Expect During A Laser Treatment Session?
During a laser treatment session for skin pigmentation, the individual can expect to wear protective eyewear to shield their eyes from the laser light. The practitioner will cleanse the treatment area and may apply a topical numbing cream to minimize discomfort. The laser device will then be directed at the targeted areas of pigmentation, emitting short bursts of light. Patients may feel a mild tingling or snapping sensation during the procedure, but discomfort is generally minimal.
The duration of a laser treatment session for skin pigmentation can vary depending on the size and severity of the treated area. Typically, sessions last between 15 minutes to an hour, although this may vary based on the specific treatment protocol and individual needs.
To manage any discomfort during laser treatment, practitioners may offer various pain management options, including topical numbing creams, cooling devices, or in some cases, oral pain medications. Additionally, newer laser technologies often incorporate built-in cooling systems to enhance patient comfort during the procedure.
Post-Treatment Care
Immediate care after treatment:
After laser treatment for skin pigmentation, individuals may experience redness, swelling, and a sensation similar to a mild sunburn in the treated area. It's essential to follow post-treatment instructions provided by the practitioner, which may include applying soothing skincare products, avoiding sun exposure, and using sunscreen regularly.
Long-term care and maintenance:
Long-term care and maintenance following laser treatment for skin pigmentation involve protecting the skin from sun exposure by wearing sunscreen with high SPF, avoiding tanning beds, and practicing a consistent skincare routine. Depending on the individual's response to treatment and the severity of their pigmentation concerns, additional maintenance treatments may be recommended to maintain optimal results.
Follow-up appointments:
Follow-up appointments with the treating practitioner are essential to monitor progress, assess treatment outcomes, and address any concerns or complications that may arise. These appointments also provide an opportunity to discuss further treatment options or adjustments to the treatment plan based on individual needs and goals.
Alternative Treatments and Comparisons
Comparison with other treatment options (e.g., topical creams, chemical peels)
When considering treatment options for skin pigmentation, individuals may encounter alternatives such as topical creams and chemical peels. While topical creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone or retinoids can help fade pigmentation over time, they may require prolonged use and may not be suitable for all types of pigmentation. Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to exfoliate the skin and improve its appearance. However, these treatments may also have limitations and varying degrees of effectiveness depending on the severity of pigmentation.
Laser treatment offers several advantages over alternative options for skin pigmentation. Unlike topical creams, which may take weeks or months to show results, laser treatment can yield noticeable improvements in pigmentation after just a few sessions. Laser therapy can target specific areas of pigmentation with precision, making it suitable for treating localized areas of concern. Furthermore, laser treatment is a non-invasive procedure that typically requires minimal downtime compared to more aggressive treatments like chemical peels or surgical procedures.
Conclusion
Laser treatment offers a promising solution for addressing various skin pigmentation concerns. Throughout this discussion, we've explored the mechanisms of laser therapy, safety considerations, treatment expectations, and post-treatment care. While laser treatment may present certain risks and discomfort, its efficacy in targeting pigmentation issues is well-established. By consulting with a qualified healthcare professional, individuals can make informed decisions about whether laser treatment is the right option for their skin concerns. Overall, with proper precautions and realistic expectations, laser therapy can provide safe and effective results, helping individuals achieve smoother, more even-toned skin.